A creative person with an investigative attitude. Skills developed at University, and within BAE Systems have enabled me to gain an appreciation of the “System of Systems” approach to Engineering, as well as the Engineering Life Cycle and the part that Human Factors plays within the system. I always undertake my work with an analytical yet determined approach in order to contribute to a team. Professionally registered. Available for employment world-wide.
Major project
How Does Motivation Affect eHealth Behaviour?
The Theoretical Basis Behind the Question
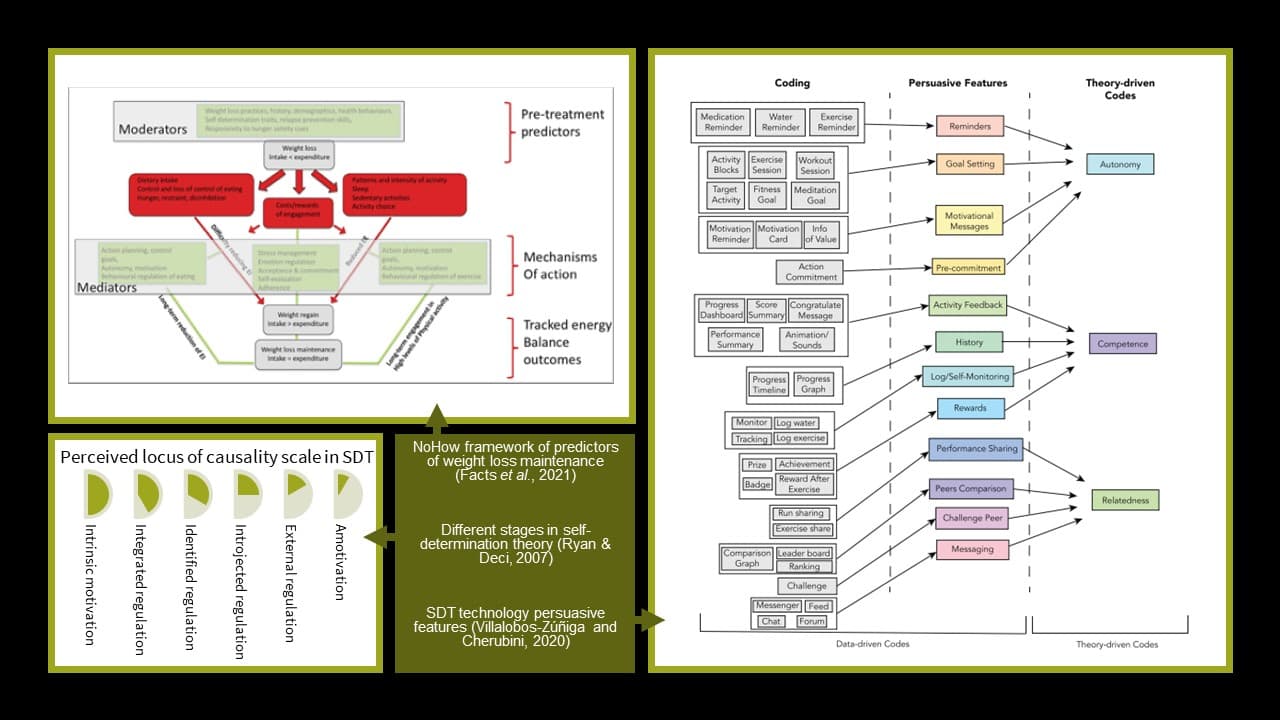
The NoHow project framed the research space of this study when it found that 80% of people having lost 10% of their bodyweight re-gained it over the next two years. With a proceeding workshop reviewing the numerous outputs finding that "developing the skills to self-manage energy balance behaviours leads to more effective weight loss maintenance,". People are able to lose weight, however, without the right motivation are unlikely maintain the positive outcome over time.
Works by Dacy and Ryan for the last 40 years have solidified the definition of motivation psychology, termed Self-Determination Theory (SDT), and form the basis of our study into how motivation affects eHealth behaviour. Works by Villalobos-Zúñiga and Cherubini in 2020, related this theory to health behaviour technology using a taxonomy of 12 persuasive features common to all “Apps That Motivate”. Our study was designed to explore the link between motivation and technology use for health behaviour or eHealth. Our study aims were:
1. Assessing the measures for motivation.
2. Understanding if motivation affects what eHealth technology people use.
The 12 persuasive features became 12 Technology types and SDT motivation variables were identified using the sources above. Relevant demographic data was identified and included (age bracket, sex, exercise or diet focus, individual or group focus, body mass index). Participants were also asked to self-declare if they were under the care of a medical professional. Care was taken to use a mixed methods approach wherever possible i.e. Likert scales, checkboxes and free text responses were taken for motivation and technology types. The survey was anonymous and used the Survey Monkey platform.
Participant Recruitment, Sample Size
The poster above was placed in gyms and sports clubs, it was also shared on private Facebook diet and exercise groups. 62 people started the questionnaire, 23 did all the mandatory questions and 18 completed all the questions satisfactorily after outlier analysis was conducted, leaving a sample size of 18.
Objectives and Data Analyis Framework
Objectives 1 and 2 answer Aim 1 and 2-5 answer Aim 2.
Objective 1: Is there a correlation or directional comparison between motivation regulatory style and the type of goal we set for ourselves?
A Spearman’s rho test for correlation was undertaken to compare the difference between two motivation measures the Situation Motivation Scale (SIMs) and the Treatment Self-Regulation Questionnaire (TSRQ) to understand if there was the expected correlation between similar SDT based motivation scores from different measurements with the present sample.
Freedman’s analysis of variance was also undertaken to understand if the distribution for motivational measures was similar or statistically different in the expected direction.
Objective 2: How do qualitative goals compare to the measured Motivation regularity scales and goal types?
The free text goal responses were coded into groups using NVivo according to estimated goal type. directionality was ascertained by comparing the median for each group.
Objective 3 How does the degree to which a person is aligned to a particular motivation regulatory scale or goal type affect whether they choose to use a particular technology type or not?
A Mann-Whitney U test was undertaken to compare the difference between each technology type use and disuse and each motivation measure.
For the statistically significant results, an exploration using NVivo word frequency was undertaken within the relevant technology type.
The most prevalent word was then explored using an Nvivo text search query for insight into emotions and technologies associated with the technology type category within the free text favourite technology responses for each participant who used that type over the last two weeks.
Objective 4: Using qualitative data what type of motivation do people with different types of eHealth behaviour have?
Free text technology responses categorised Positive Emotion, Negative Emotion and External Emotion were analysed for insight into technology contributions.
All the different applications or technologies named within each group were analysed in the same way as the text search query in Objective 3.
Objective 5: How does the degree to which a person is aligned to a particular motivation regulatory scale or goal type affect the number of technology types they use?
A Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA was undertaken to compare the difference between those who used a greater variety of technology types and each motivation measure to the number of technology types selected.
Summary of Detailed Results
A Spearman’s correlation showed a moderate positive correlation between introjected regulation and introjected goals. Those students who were more aligned to introjected regulation also were more aligned to introjected goals. (rho=0.475, p=.046, α=.05)
A Spearman’s correlation showed a moderate positive correlation between external regulation and autonomous goals. Those students who were more aligned to external regulation were more aligned to both Autonomous goals. (rho=.472, p=.048, α=.05).
A Freedman’s two-way analysis of variance for related samples showed a significant difference the distribution between Motivational Regulatory Scale and Goal type. (Chi Square =84.989, df=7, p=000, α=.05) It showed a large effect size based on Cohen’s interpretation guidelines W=0.675. Post hoc pairwise comparisons showed that 18 of the 28 groups were different and 10 the same in the expected direction.
Objective 2 Results:
Positive, external and negative emotion (3 groups) were significantly different for Amotivated Goal TSRQ scores (Mann-Whitney U=8.919, p=.012, α=.05). Post hoc pairwise comparisons indicate that the rating for external emotion is significantly higher than for positive emotion, not significantly different between positive and negative or negative and external emotion with a medium effect size 0.54.
Effect size (r=z/√n where n = total number of observations) = (-2.289)/√18 = 0.54 = medium effect size.
Objective 3 Results:
There is a significant difference in the level of Amotivated motivation according to whether a person chose to share their performance. (U=9.5, p=0.022, α=0.5) Effect 0.54 = medium effect size. The median Amotivated motivation was higher for those that did not share their performance using technology.
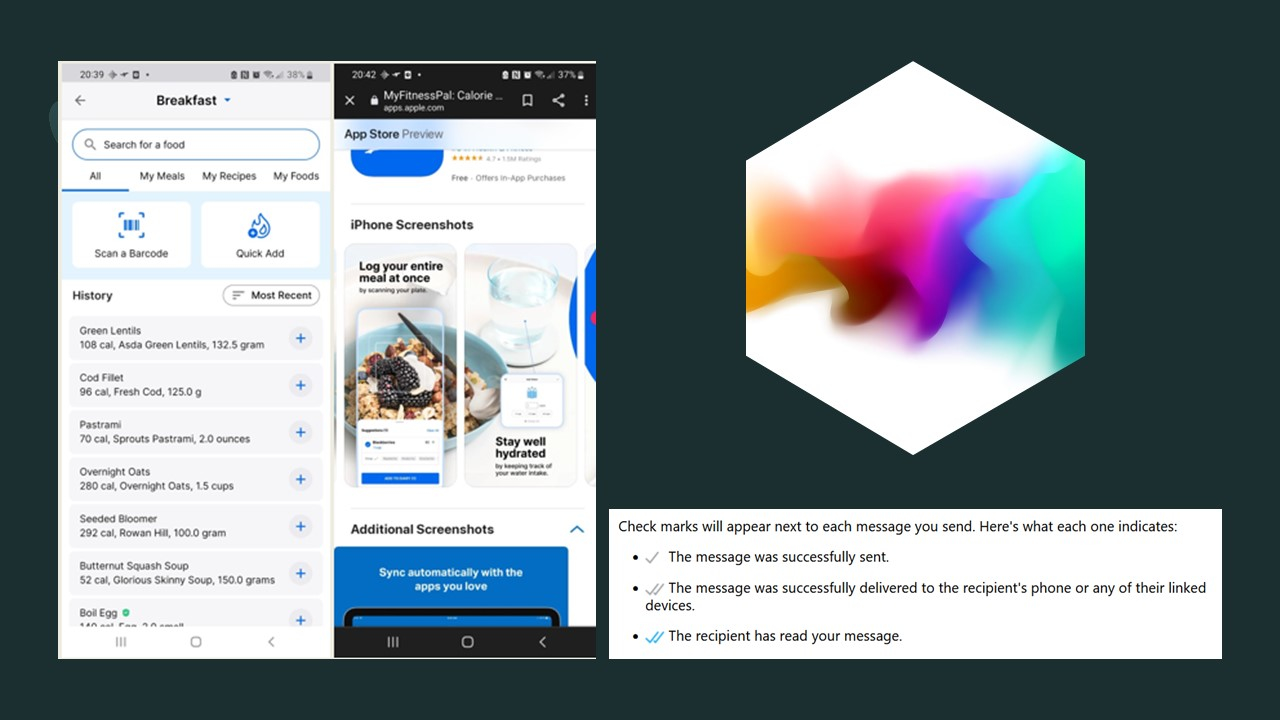
MyFitnessPal was used by two participants for the logging and monitoring of calories and nutrition. Nutracheck was also used for this purpose. 4 out of 10 comments included this type of logging for the logging and monitoring technology type.
Objective 5 Results:
There is no significant difference in the degree to which a person is aligned to a particular motivation regulatory scale or goal type when comparing the distribution across all measures of variety of technology used (Exact number of technology types used, instances split into 4 groups, instances split into 3 groups).
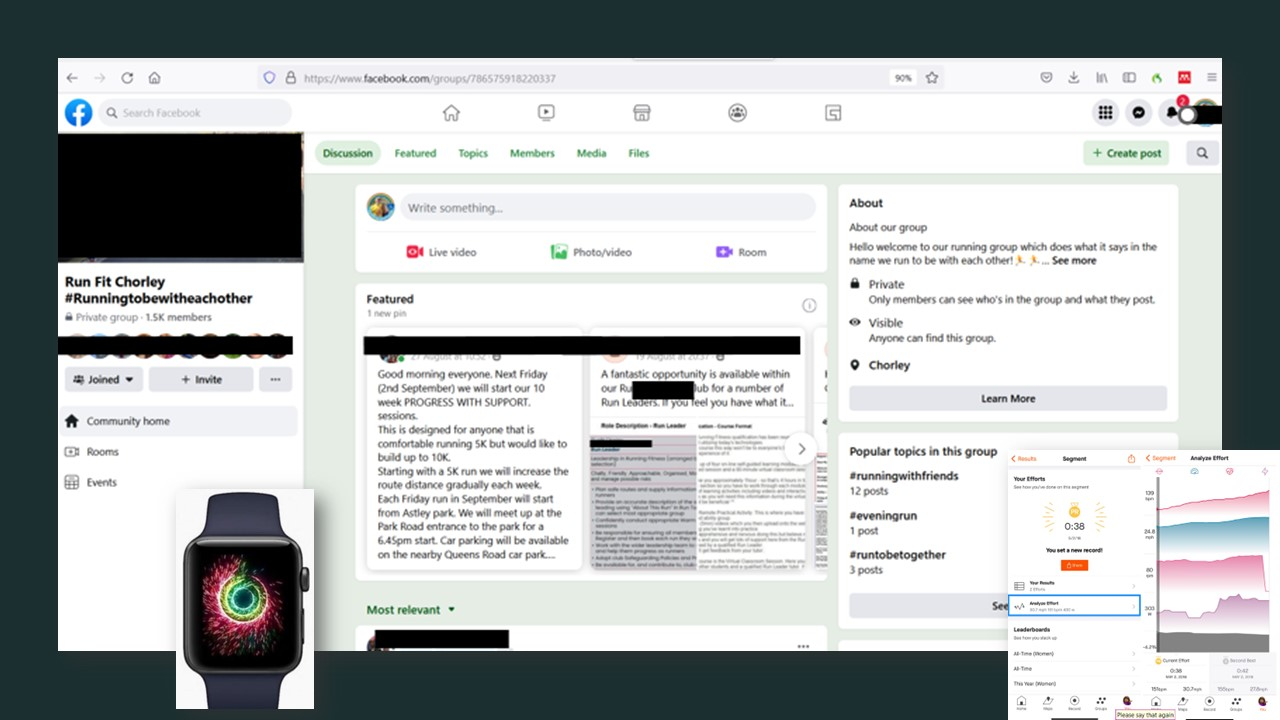
Objective 4: Positive Emotion Design Features Review (Features Apple Watch - Close Your Rings bottom left, Facebook group, and Strava -My Leader Board bottom right)
Close Your Rings – Apple Watch and Fitness App, My Leader Board - Strava , Facebook Group posts were found to have the most positive language surrounding their usage descriptions.
Close Your Rings – Apple Watch and Fitness App:
Pace and distance throughout a run, exercise and movement competition, rings close and see the detail of exercise, weekly progress reports and sending a completed circle are all mentioned in positive comments. The rings feature was mentioned the most and so investigated here.
The rings are displayed on the apple watch and available to give feedback at all times to the user who can always see their wrist. When all the rings close a fireworks animation is played and when each ring closes an achievement is displayed. When logging exercise it can be time, calorie, distance, or own goal based. The own goal element allows people used to undertaking the exercise to add their own reason for completing the session, thus reducing the feeling of control created by the application. The ability to share the achievement with others is embedded in the software. Easy to read icons and reminders encourage you to complete/highlight what needs to be done to “close your rings”. This could be seen as controlling by the user, however, the element of competition gave the control over to another person to take advantage of the relatedness motivation sphere hence the positive comment. This offers control over the activity with clear and immediate feedback inducing a flow state (Holton and Holton, 2015).
My Leader board – Strava:
"Using my leader board", "Add people to your runs and compare your performance", "Couple of medals as well route and average pace reviews", were all mentioned in positive comments about Strava. These are all part of the My Segment results feature on the Strava application. Strava describes “If you're sharing from the mobile app, you can choose your friend from your list of followers. If your friend isn't on Strava yet, you can select which application you'd like to use to share your activity seen using the blue square". The freedom to choose whether to add the person and also the ability of the app to recommend a group encourages the relatedness psychological need by nudging interaction with a group, where the positive comments were based in the study sample(Ryan and Deci, 1985; Deci and Ryan, 2000; Gunnell et al., 2014).
Running Club Facebook Group:
Facebook Group posts were found to have the most positive language surrounding their usage descriptions, using language such as "supportive", "like to", and "encourage". Further investigation into the mechanisms behind these positive emotions were not covered in this study.
Objective 4: Negative and External Emotion Design Features (MyFitnessPal left and WhatsApp and Facebook messenger Read Reciepts)
Read Recipes - Facebook and WhatsApp Messenger, Nutrition Logging – MyFitnessPal were found to have the most negative language surrounding their usage descriptions, whereas, FitBit Challenges and Garmin Move reminders had the most externally motivated langauge surrounding their usage descriptions. Further investigation into the mechanisms behind these negative and external emotions were not covered in this study.
Critical analysis
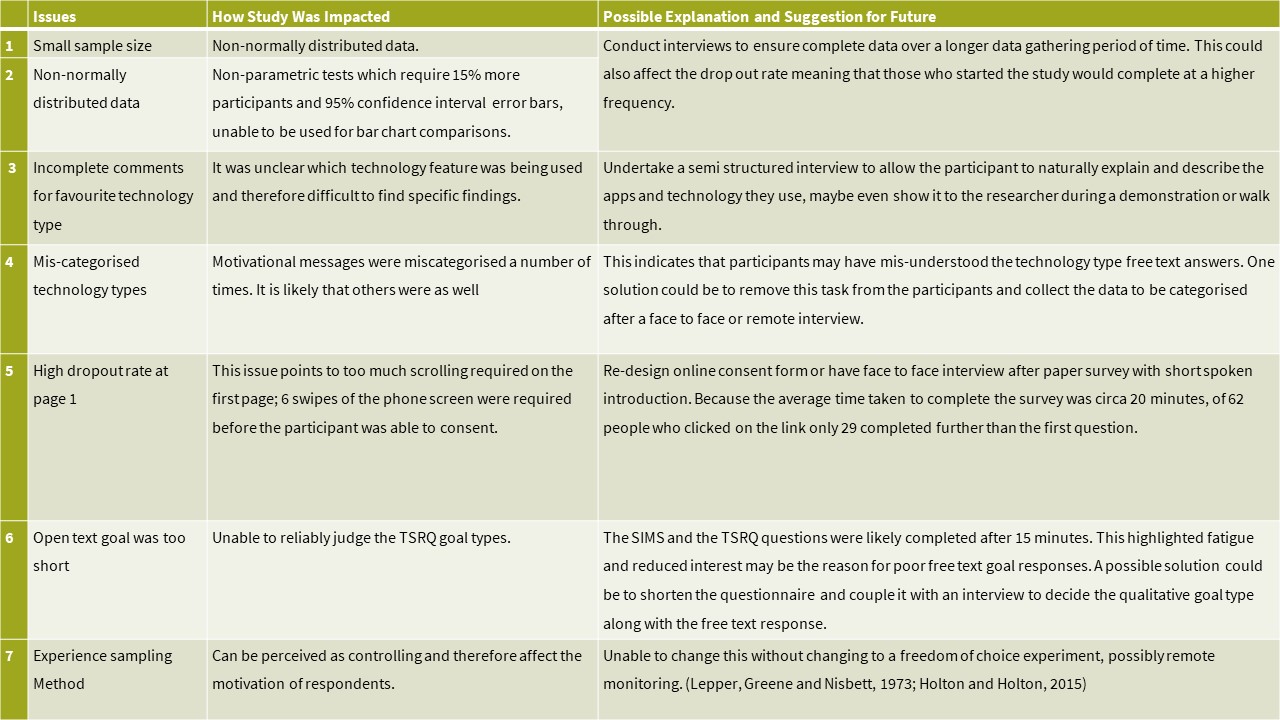
The design of the survey balanced the need to gather data, be short for completion before a planned task and gather the most important data first. This was a difficult balance and other methodologies with more time would perhaps be more appropriate.
A test was conducted to investigate if these incoherences could be rectified by using a different methodology. After completing the consent form and reading the information sheet The SIMS, TSRQ, free text main healthy activity goal as well as the demographic data. An initial scoping interview was held. The semi structured interview format started with an open first question bounded to the last two weeks and then the information in the answer was used to direct prompts with a view to completing the technology type data within the codebook of Nvivo rather than the participant using an online survey tool.
This was found to elicit a far richer data set and address issues 2, 3 and 4 directly whilst indirectly improving issues 1, 5 and 6. This warrants further investigation in future work.
Future work
Further analysis of areas of strength and weakness of apps/features identified in this study would be beneficial, namely:
- Close Your Rings – Apple Watch and Fitness App and My Leader board – Strava.
- Fitbit Challenges and Garmin Move Reminder.
- WhatsApp Route Sharing and Facebook Posts; of particular interest is how page content and design and leadership in sports group social media can affect the user experience and motivation of a group member.
-Facebook and WhatsApp Messenger Read Receipts and MyFitnessPal Nutrition Logging.
Issues with remote assessment, low completion rate and sample size, participant understanding of the technology type questions and time sensitive requirements of the measures (i.e. directly before a healthy activity) should be investigated assessing suitability different methods addressing these issues such as;
-Semi structured interviews and repeated measures assessment design.
-Freedom of choice experimental design – observation of which application people choose from a list with different time instances covered, e.g week, day and hour.
-Walkthroughs with participants using their technology features with remote monitoring/diary-based methodologies.
Claudia Hargreaves
Major project
How Does Motivation Affect eHealth Behaviour?