First, all severe PTW-related accidents from Safer Wheels are investigated to clarify common human factors, collision types, and PTW vehicle characteristics in different types of PTW serious accidents. The second objective is to conduct a broad and in-depth survey of existing PTW ADAS technologies to determine how they work during accidents. The third objective is to score the ADAS mentioned in the study. In particular, based on the data obtained from the first two objectives, the possible performance of the ADAS in each type of accident is comprehensively evaluated. The reliability ranking of existing ADAS technology is obtained and this ranking is used to discuss which ADAS has the best performance in recent PTW accidents combined with this analysis to provide more valuable design lessons for ADAS currently in development.
Major project
The Future Development of Motorcycle ADAS based on needs identified from Motorcycle Accident Data
The cornering ABS working in band/curve
The dotted line is where the rider would go if the rider hit the brakes with regular ABS. The solid line is where the rider should go, and where cornering ABS/lean angle-sensitive ABS tries to take you.
The picture of performance of ABS and Cornering ABS in same curve
the picture showed the cornering ABS working better than ABS when passing the curve/bend. the motorcycle using cornering ABS can keep the track well when passing the curve.
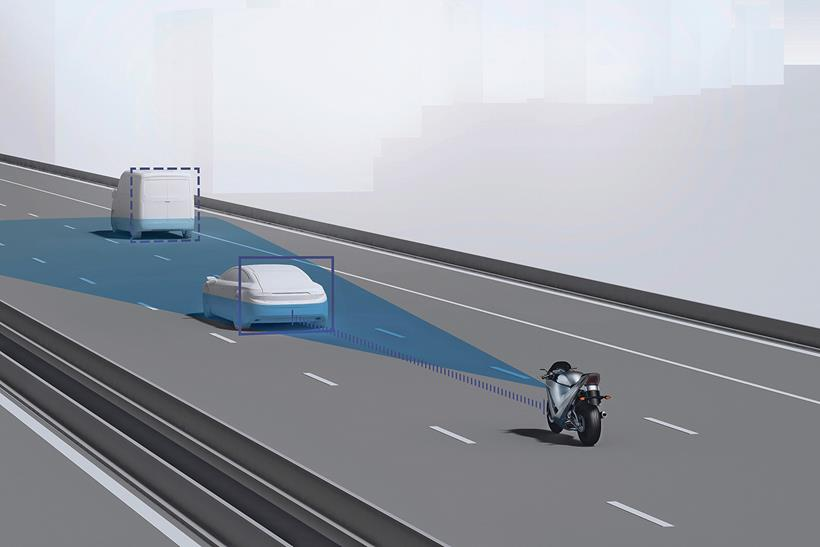
Schematic diagram of a working motorcycle radar
A radar sensor consists of two main components: a transmitter and a receiver. Radio waves bounce off any object they hit in the area and reflect to the receiver. By measuring these reflections - their width, the direction they came from, and the time it takes them to return - the radar "sees" objects, including recording how fast and in which direction they move.
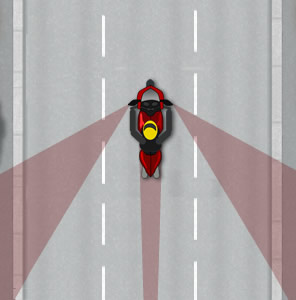
Blind spot warning working in straight road
The red shaded area shows the motorcycle's blind spots
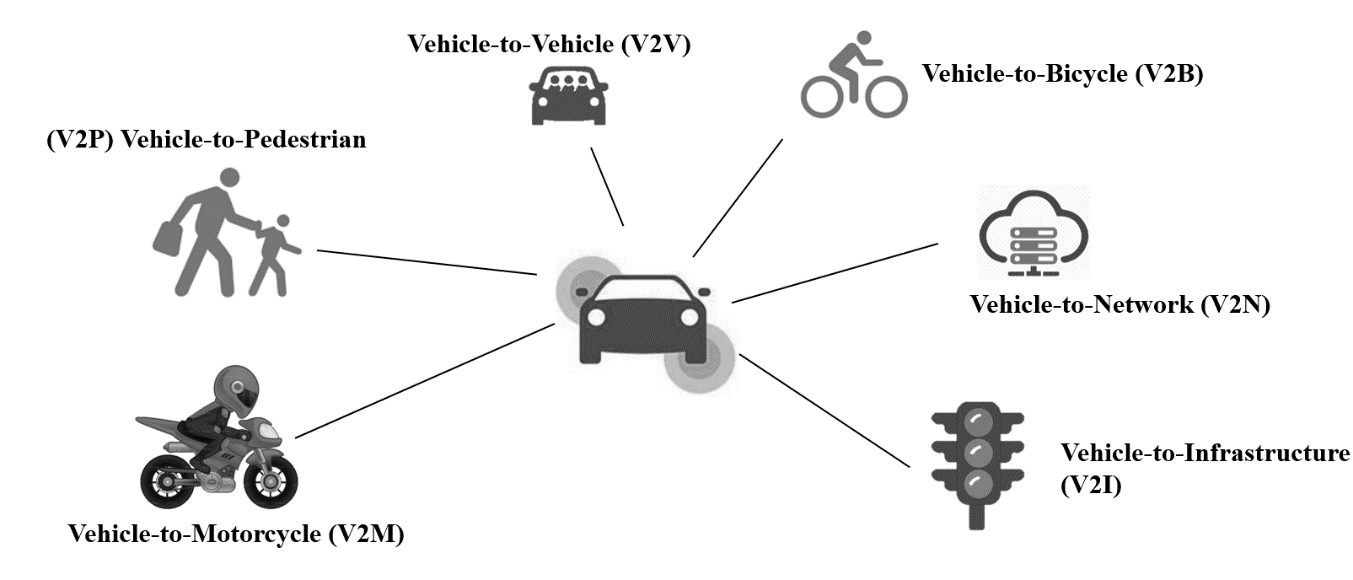
Overview of Vehicle-to-Everything Technology
Intelligent transportation systems based on V2X and C-ITS networks are the most promising motorcycle traffic safety solutions under development. C-ITS stands for Collaborative Intelligent Transport Technology, which uses more advanced communication technologies to connect all road users in a traffic environment. The basic working principle of this technology is to communicate primary state data (position, speed, direction angle, etc.) with other vehicles and infrastructure through V2X communication. Riders are alerted when they cross the tracks of drivers or other vulnerable road users and instruct riders to slow down to avoid other road users. The DSRC system consisting of Roadside Unit (RSU) and On-Board Unit (OBU) was identified as the fastest and most stable mode of communication. Even at extremely high speeds, stable communication can be established between all road users in the area, guaranteeing extremely low communication delays.
Qihang Yang
Major project
The Future Development of Motorcycle ADAS based on needs identified from Motorcycle Accident Data